Hi
lti
HIT-
RE
50
0-
SD mortar
wi
th
r
ebar (as anchor)
09
/ 2014
Thes
e pages
are par
t of
the Anchor
Fas
tening
Technology
Man
ual
is
s
ue
September
2014
539
Basic design shear resistance
Design steel resistance V
Rd,s
Data according ETA-07/0260,
iss
ue
2013-06-26
Anchor size
Ø8
Ø10
Ø12
Ø14
Ø16
Ø20
Ø25
Ø28
Ø32
V
Rd,s
BSt 500
S
[kN]
9,3
14,7
20,7
28,0
36,7
57,3
90,0
112,7
147,
3
Design concrete pryout resistance V
Rd,c
p
= lower value
a)
of k
N
Rd,p
and k
N
Rd
,c
k = 1 for h
ef
< 60 mm
k = 2 for h
ef
≥
60 mm
a)
N
Rd,p
:
Design combined pull-out
and concrete cone resistance
N
Rd,c
:
Design
concrete cone resistance
Design concrete edge resistance
V
Rd
,c
= V
0
Rd,c
f
B
f
ß
f
h
f
4
f
hef
f
c
Data according ETA-07/0260,
iss
ue
2013-06-26
Anchor size
Ø8
Ø10
Ø12
Ø14
Ø16
Ø20
Ø25
Ø28
Ø32
Non-cracked concrete
V
0
Rd,c
[kN]
5,9
8,6
11,6
15,0
18,7
27,0
39,2
47,3
59,0
Cracked concrete
V
0
Rd,c
[kN]
4,2
6,1
8,2
10,6
13,2
19,2
27,7
33,5
41,8
Influencing factors
Influence of concrete strength
Concrete strength
des
ignation
(ENV 206)
C 20/25
C 25/30
C 30/37
C 35/45
C 40/50
C 45/55
C 50/60
f
B
=
(f
ck,cube
/25N/mm²)
1/2
a)
1
1,1
1,22
1,34
1,41
1,48
1,55
a)
f
ck,cube
= concrete compressive strength, measured
on cubes with 150 mm side lengt
h
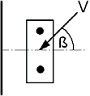
Influence of angle between
load
appl
ied and the direction perpendicular to the free edge
Angle ß
0°
10°
20°
30°
40°
50°
60°
70°
80°
≥
90°
2
2
5
,
2
sin
cos
1
¸
¹
·
¨
©
§
V
V
f
D
D
E
1
1,01
1,05
1,13
1,24
1,40
1,64
1,97
2,32
2,50
Influence
of base material
thickness
h/c
0,15
0,3
0,45
0,6
0,75
0,9
1,05
1,2
1,35
≥
1,5
f
h
=
{h/(1,5
c)}
1/2
≤
1
0,32
0,45
0,55
0,63
0,71
0,77
0,84
0,89
0,95
1,00